深圳大学物理与光电工程学院,广东 深圳 518060
在现有单次测量极高速成像方法中,直接成像方法的分辨率高但探测系统复杂,而计算成像方法探测系统简单但易损失空间分辨率。因此,提出一种基于偏振编码的极高速成像技术。所提成像系统利用半波片阵列和偏振片阵列对入射飞秒脉冲、出射飞秒脉冲和动态事件进行偏振编码,并通过线性方程组解码极高速动态的时序图像。通过构建光学模型并仿真,精确还原了多幅图像,验证了所提方案的可行性,理论摄影频率在1013 frame/s以上,本征空间分辨率可达114 lp/mm。所提成像系统结合了直接成像和计算成像系统的优势:线性方程组精确求解,不会导致光学系统分辨率损失;时序图像叠加使探测结构只需分光不需要对不同时刻的图像进行空间上的分离,简化了探测器的结构。该极高速成像系统的时间分辨率仅受脉冲宽度限制,可以实现飞秒级动态事件的探测,并且随着脉冲宽度的缩短,其时间分辨率可以得到进一步提升。
成像系统 偏振编码 极高速成像 线性方程组 时序图像 飞秒脉冲 光学学报
2022, 42(20): 2011002
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics, Xi’an, China
2 University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
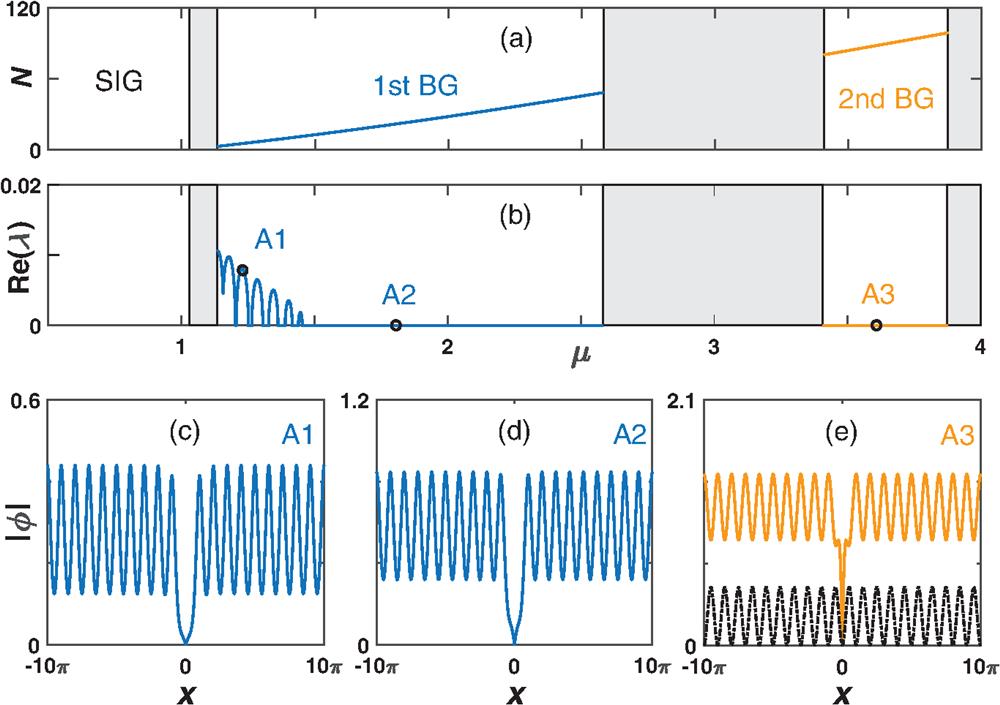
Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) exhibits a variety of fascinating and unexpected macroscopic phenomena, and has attracted sustained attention in recent years—particularly in the field of solitons and associated nonlinear phenomena. Meanwhile, optical lattices have emerged as a versatile toolbox for understanding the properties and controlling the dynamics of BEC, among which the realization of bright gap solitons is an iconic result. However, the dark gap solitons are still experimentally unproven, and their properties in more than one dimension remain unknown. In light of this, we describe, numerically and theoretically, the formation and stability properties of gap-type dark localized modes in the context of ultracold atoms trapped in optical lattices. Two kinds of stable dark localized modes—gap solitons and soliton clusters—are predicted in both the one- and two-dimensional geometries. The vortical counterparts of both modes are also constructed in two dimensions. A unique feature is the existence of a nonlinear Bloch-wave background on which all above gap modes are situated. By employing linear-stability analysis and direct simulations, stability regions of the predicted modes are obtained. Our results offer the possibility of observing dark gap localized structures with cutting-edge techniques in ultracold atoms experiments and beyond, including in optics with photonic crystals and lattices.
Bose–Einstein condensates optical lattices photonic crystals and lattices self-defocusing Kerr nonlinearity dark gap solitons and soliton clusters Advanced Photonics
2019, 1(4): 046004
华南师范大学 物理与电信工程学院, 广州 510006
为了满足光偏振态分振幅测量模块(DOAP)对分光棱镜复杂且严格的加工要求, 采用在经典DOAP透射光路及反射光路各引入一块波片的方法, 组成改进后的光偏振态测量模块。推导了新的仪器矩阵表达式, 通过分析波片参量对仪器矩阵条件数的影响, 得到了最佳波片的参量及其关系。结果表明, 优化后的斯托克斯椭偏仪测量薄膜样品的厚度和折射率的标准差分别为0.1nm和0.001。通过选择波片的最佳方位角或相位延迟量可以实现斯托克斯椭偏仪仪器矩阵的优化, 从而提高系统的测量稳定性及可靠性。
测量与计量 光偏振态测量 条件数 斯托克斯参量 measurement and metrology optical polarization measurement condition number Stokes parameter





